
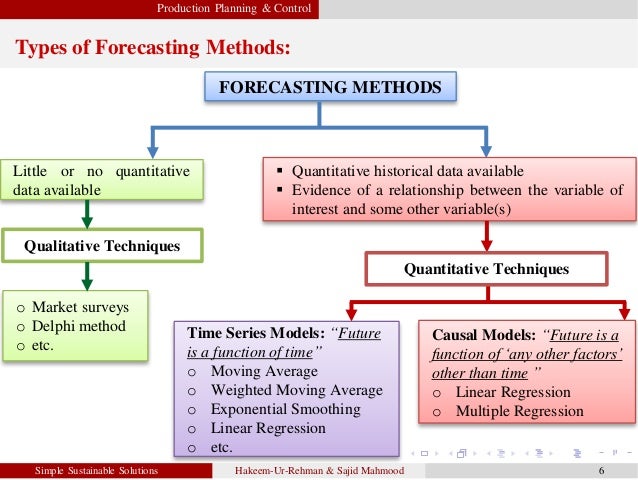
They are usually applied to intermediate- or long-range decisions. Qualitative forecasting techniques are subjective, based on the opinion and judgment of consumers and experts they are appropriate when past data are not available. 5.1 Performance limits of fluid dynamics equationsĬategories of forecasting methods Qualitative vs.1.10 Geometric Extrapolation with error prediction.In some cases the data used to predict the variable of interest is itself forecast. In any case, the data must be up to date in order for the forecast to be as accurate as possible. Risk and uncertainty are central to forecasting and prediction it is generally considered good practice to indicate the degree of uncertainty attaching to forecasts.

Usage can differ between areas of application: for example, in hydrology the terms "forecast" and "forecasting" are sometimes reserved for estimates of values at certain specific future times, while the term "prediction" is used for more general estimates, such as the number of times floods will occur over a long period. Both might refer to formal statistical methods employing time series, cross-sectional or longitudinal data, or alternatively to less formal judgmental methods. Prediction is a similar, but more general term. A commonplace example might be estimation of some variable of interest at some specified future date. Making predictions based on available dataįorecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data and most commonly by analysis of trends.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
